The RT-PCR test is an accurate test for diagnosing infectious diseases, especially COVID-19. The acronym stands for reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. This test has become immensely popular since the emergence of the Coronavirus pandemic. A positive test is a reliable indication that you suffer from COVID-19. On the other hand, a negative test probably means good news—that you have been spared this disease. Read this article to know exactly how the RT-PCR is done and what you can expect.
What is the RT-PCR test?
Before learning how the RT-PCR is done, you must first know what it is. A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test is a quick and precise way to diagnose genetic variations and infectious diseases, most prominently COVID-19. The basic premise behind the working of this test is to locate the DNA or RNA of a pathogen that causes the disease. The test can also discover abnormal cells in a sample to diagnose a disease.
The test facilitates the detection of genetic material from a particular organism, usually a virus. This is how RT-PCR is done. The presence of a virus can easily be detected with this test if the person undergoing it had the virus at the time of the test. Medical experts can also identify virus fragments even after the patient has recovered from this test.
Who should get tested for COVID-19?
As we have already learned, this test can detect infectious diseases like COVID-19. So, the experts recommend this test if you suffer from the following symptoms:
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Diarrhoea
- Runny nose
- Muscle pain
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Loss of taste
- Loss of smell Congestion
- Nausea or vomiting
- Congestion
- Nausea or vomiting
How does RT-PCR detect COVID-19
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is the culprit agent behind COVID-19. It is an RNA virus that multiplies and survives in a healthy cell after infiltrating it. The SARS-CoV-2 RNA can be accurately detected with the help of an RT-PCR test. In this test, the conversion of the RNA takes place to DNA via the ‘reverse transcription’ process. This conversion is the key to the detection of viruses.
Medical experts detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the respiratory specimens when the patient is in the infection’s acute phase. Samples are collected for various respiratory regions like:
- Nasal
- Nasopharyngeal swabs
- Sputum
- Lower respiratory tract aspirates
- Bronchoalveolar lavage
- Nasopharyngeal wash/aspirate or nasal aspirate
Experts treat the collected sample with chemical solutions to remove certain unwanted substances. After collection, the expert extracts only the RNA from the collected sample.
How is the RT-PCR done?
The question ‘how is RT-PCR done’ can be answered in the following three key steps:
Sample collection
Here, a healthcare provider collects respiratory material from the nose by inserting a swab. A swab is a soft tip on a flexible and long stick.
Nasal swabs and nasopharyngeal swabs are the two types of swabs used. The former collects nostrils samples while the latter collects deeper nasal cavity samples. Both types are suitable for collecting material. After collection, the swab is sealed in a tube, which is sent to a laboratory for further testing.
Extraction
The swab is sent to a laboratory in a sealed tube after collection. After receiving the sample, the laboratory scientist isolates or extracts the genetic material from the rest of the sample material.
PCR
In this step, special chemicals are used along with a PCR machine. Here, the amount of the targeted genetic material is amplified due to the hot and cold cycle. After plenty of cycles, several copies of a small portion of the SARS-CoV-2 genetic material are created.
One of the tube chemicals results in the production of fluorescent light in case there is SARS-CoV-2 in the sample. When the amplification becomes significant enough, this signal can be detected by the PCR machine. Scientists use this special software to interpret the signal as a positive test result.
Method of RT-PCR testing
There are two different ways to get a test sample. The method Of RT-PCR testing can take two forms—blood test and nasal swab.
Blood test
Here, a health care professional extracts blood from your body by inserting a small needle into your vein. When the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood from the body is collected in a vial or test tube. This small amount of blood serves as the sample. The whole procedure takes just a few minutes, and you may feel a little pain when the needle is inserted.
Nasal swab
Here, samples are collected from the nostrils by a healthcare expert. The samples can be collected either from the front or the back of your nostrils. The samples may also be extracted from the nasopharynx, which is the upper part of the throat/nose. This is the most common way of conducting RT-PCR testing.
The procedure of the nasal swab method of RT-PCR testing is as follows:
- The healthcare professional will tilt your head back.
- Then, the expert will insert a swab inside the nostril gently.
- The swab will be rotated inside the nostril.
- The swab must be left inside for 10 to 15 seconds.
- The swab is removed after 10 to 15 seconds, and the process is repeated in the other nostril.
How do the test results arrive?
A real-time RT-PCR setup has to undergo 35 cycles as per the standard procedure. As such, around 35 billion new copies of the viral DNA sections will be created. These copies pertain to each sample virus strand.
As new copies are created, marker labels attach to the DNA strands. Afterwards, a fluorescent dye is released. The machine’s computer measures this dye, and you can see this on the screen in real-time.
The computer tracks the amount of sample fluorescence after each cycle. When this amount exceeds a certain level of fluorescence, the presence of the virus is confirmed.
Scientists may also monitor how quickly this level is reached, that is, how many cycles it takes to reach this level. The fewer cycles it takes, the more severe the disease.
What is the meaning of the RT-PCR result?
A positive test result means a significant likelihood that the person is affected by Coronavirus. Sometimes, a person may be asymptomatic and display no symptoms of COVID-19, even after appearing positive on the test.
People who test positive may display only mild symptoms in some cases. In such cases, patients can recover safely in their homes without being admitted to a hospital. However, if the symptoms become severe, the person must immediately contact a healthcare provider.
A negative test result means a considerable likelihood that the person is not affected by Coronavirus. However, it could also mean that the person did not have the virus when the test was taken. So, if people receive negative test results, it does not necessarily mean that the test was ineffective.
This test is not perfect, and it is possible that the test was unable to detect the Coronavirus. So, as pointed out by clinical experts, a negative test is not a guarantee that a person is safe.
The person may still be exposed to the Coronavirus after undergoing the test and may spread the virus. As such, one must continue to take protective steps even after receiving negative RT-PCR test results.
How long after being infected do you test positive for COVID-19?
Owing to the RT-PCR test’s immense sensitivity, detecting extremely small virus material amounts is possible. This means fragments of the Coronavirus can be detected even after the patient has recovered from COVID-19 and is no longer contagious. People may test positive for a while after they contract the illness.
People whose immune systems have been compromised may experience prolonged sickness. Healthy individuals may also be re-infected by the virus.
Difference between the PCR and antigen tests
There are two types of tests for the detection of COVID-19.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): This detects the presence of the virus’s genetic material. The test also identifies the presence of the virus fragments. According to most healthcare experts, this is the most accurate and reliable test we have. The performance of this test can go on for hours.
Antigen test: This detects protein bits on antigens’ surfaces. Antigens are a type of virus. The test’s performance duration ranges from 15 minutes to half an hour. They are highly accurate but only within the first few days of the onset of symptoms.
Where to get tested?
If you display COVID-19 symptoms or were around positively tested people, get yourself tested immediately. Also, talk to your doctor about your condition and the possible consequences.
Your doctor will provide you with certain instructions after reviewing your symptoms or circumstances. This could be done either face to face or via online or a video call. If necessary, the doctor will recommend that you get a test done. The doctor may suggest a testing facility or may help you find one.
Make sure to communicate with the facility, if possible, to make preparations beforehand. You can also learn about the details of testing facilities by visiting websites on the internet.
What to expect from this test
A sample of your mucus or saliva shall be taken from your nose or throat by a healthcare expert. This is required for diagnostic testing. The collection may happen at a healthcare facility like a hospital, a doctor’s private clinic, or at a drive-up testing centre.
Professionals from home service providers such as MyGate can also be invited to a place of your convenience for sample collection.
For the nose swab, a healthcare professional will insert the cotton tip of a thin stick inside your nose. This is in order to collect a mucous sample. You may feel a slight discomfort, but it’s not a big deal.
A saliva sample is comparatively easier and more comfortable. All you have to do is spit in a tube multiple times. This way, a sample of your saliva gets collected for laboratory analysis.
If there is a need for a blood test, then expect a needle to be inserted into a part of your body, usually the arm. You may feel slight pain during this insertion but not to the degree to make you concerned.
Accuracy of the RT-PCR results
The results of the RT-PCR are not 100% accurate. False positives and negative incidents have been reported across the world. Positive results may be an indication of Coronavirus but may not entirely be accurate.
However, this does not mean that you start doubting this test. Despite not being completely precise, the test is still quite reliable. In fact, this is the best testing method we have so far to detect COVID-19.
Pros of RT-PCR testing
RT-PCR testing is an accurate and reliable test that has the following pros:
Minimally invasive– You can have this test performed in a minimally invasive manner by using nasal swabs.
Possibility of isolation– The RT-PCR can sometimes be taken from the car or home of the patient, thereby facilitating proper social distancing.
Reduced false negatives cases– Nasal swabs, especially deep ones, will have fewer false negatives compared to other tests.
Cons of RT-PCR testing
The method of RT-PCR testing is not entirely flawless. Below are the various cons of RT-PCR testing:
Long wait for the result– Sometimes, RT-PCR test results can take up to 1 to 2 weeks to be reported. This was the reality during the COVID-19 pandemic.
False negatives– The molecular tests have occasionally failed to detect the virus when the patient actually did have the virus. The ranging of the false positives rate is from 2 to 37 per cent.
Discomfort– Deep nasal swabs and needle insertions can be uncomfortable for children and older adults.
Coronavirus or SARS-CoV 2 causes the Covid-19 disease, which is now a worldwide pandemic. One of the primary modes for combating this pandemic is rapid identification of the infected persons so that subsequent treatment can begin fast, and they can be quarantined before spreading it to others.
Symptoms that should lead to testing:
- Fever
- Chills
- Loss of breath
- Respiratory problems
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Muscle pain
- Loss of smell and taste sensations
- Headache
- Body ache
- Sore throat
- Lung congestion
- Running nose
- Diarrhoea
- Nausea
Apart from these, some infected persons may not show any signs of these symptoms, but can spread the disease nevertheless, so it is crucial to undergo testing even for these asymptomatic persons.
Some IDSA (Infectious Disease Society of America) guidelines for undergoing testing are as follows:
- If anyone has been in close contact as within 6 feet of an infected person and exposed for more than 15 minutes.
- If one has participated in any public event like mass gatherings, marriage, or any party, travelled recently, or has been confined within an enclosed area with large crowds.
- Before any major surgery or during immunosuppressive therapy, as they are more at risk.
- Before any organ transplantation or stem cell surgery.
- Before and after childbirth.
- Repeat testing in suspected individuals even when primary test results are negative.
Types of testing for Covid-19
There are multiple diagnostic tests and antibody test types for Covid-19.
Diagnostic tests are important for detecting active infection in a person. These are mainly 2 types:
- Molecular tests, like the RT-PCR test for Covid-19.
- Antigen-based rapid test for Covid.
The antigen-based test identifies typical surface antigens present within the sample using immune-chromatographic methods. Though it is effective for identifying acute cases and is handier as it can be performed at home, the sensitivity is lower than molecular methods, about 30–40 % less. Hence, it can’t be used as a confirmatory test for Covid diagnosis and needs to be followed by molecular ones.
Sample collection
Samples are typically collected by using a cotton swab, a long tube with sterile cotton attached at one end enclosed within a capped sterile tube.
The samples tested for the Covid-19 Rt-PCR test, primarily, are:
- Anterior nares (Nasal) – Samples collected from the nostrils.
- Mid-turbinate – Samples from deep within the nose.
- Nasopharyngeal – Further deeper inside the nose, adjoining the throat.
- Oropharyngeal – Deep inside the throat in the pharyngeal region, just below the mouth.
Saliva samples are also collected by the patient spitting into a sterile tube.
What is the Rt-PCR test for Covid-19?
Rt-PCR stands for Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is a highly sensitive, quantitative test for detecting even trace amounts of any viral or bacterial genetic material within the sample.
This test is the gold standard for Covid-19 virus detection and has been approved for use since February 2020.
The basic steps of an Rt-PCR test are as follows.
Extraction
The sample collected is extracted to isolate the genetic materials, typically done by adding chemicals and peptides that dispose of any proteins or chemical particles from the sample leaving behind pure genetic materials only like RNA or DNA for analysis.
Reverse transcriptase
This is an enzyme that is capable of transcribing complementary DNA strands from a single mRNA strand. This cDNA strand is then amplified and detected using PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique. This test typically can detect even a minuscule amount of RNA (as SARS-CoV is an RNA-containing virus) present within the sample and is highly specific.
The basic ingredients used for PCR set-up are as follows:
- A DNA template strand to bind to the target region of DNA and then to amplify. For Covid-19 generally, the ORF1ab gene is used as a target. This is a SARS-COV gene found in its nucleocapsid region.
- A heat-stable DNA polymerase enzyme that can synthesise new DNA strands from the mother cDNA. Generally, heat-resistant Taq polymerase isolated from thermophilic bacteria residing in volcanic regions is used for this purpose.
- Two types of DNA primers that are complementary to both the strands of the target DNA, as DNA polymerase can only bind and amplify double-stranded DNA only. Primers are single-stranded DNA fragments that are smaller in size but site-specific. Primers specific to target DNA strands are prepared in biochemical laboratories and supplied to customers.
- Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates or dNTPs, are the units of DNA. These dNTPs are polymerized by polymerase enzymes into the new DNA strands.
- A suitable buffer solution for providing an optimal chemical atmosphere for the reactions.
- Magnesium (Mg2+) or Manganese (Mn2+) cations
PCR reaction is carried within small Eppendorf tubes of approx 0.5 mL volume, within a thermal cycler. This cycler can control accurate temperatures within the reaction centre and heats and cools the tubes according to the required steps.
PCR reaction consists of repeated extreme changes in temperatures from 20 to 40 thermal cycles for a certain amount of time. These changes depend on several factors like the temperature sensitivity of the enzymes used, melting temperature (the temperature at which the double-stranded DNA separates from each other) of the DNA primers, and concentration of the Mg/Mn cations and the dNTPs.
The steps of PCR or polymerase chain reaction are as follows:
Initialization: This step includes heating the reaction chamber to a high temperature of 94–98 °C for 10 minutes to activate the Taq polymerase enzyme that reacts at this optimum temperature. This initiates the PCR.
Denaturation: This is the first step of the thermal cycle. The reaction chamber is heated to 94–98 °C and kept at it for 20 – 30 seconds. At this stage, the template DNA strands (obtained from the Reverse transcriptase stage) melt, separating from each other due to breakage of the Hydrogen bonds connecting the complementary bases resulting in two fragments of single-stranded DNAs.
Annealing: At this step, the temperature is dropped to 50–65 °C and kept at it for 20–40 seconds. As the DNA strands cool down, the primers bind to their complementary target site of the denatured DNA template strands. The temperature and holding time are very crucial, as they should facilitate the perfect hybridization of the primer with the template. The optimal temperature is generally 3–5 °C below the melting temperature of the primer DNA. A temperature lower than that will result in erroneous binding resulting in wrong DNA synthesis, whereas a higher temperature will prevent any binding at all.
Extension or elongation: This temperature depends upon the polymerase enzyme used for DNA synthesis. Taq polymerase acts at an optimum temperature of 75–80 °C (preferably 72° C). The time for complete elongation of the cDNA strand varies on the type of polymerase enzyme used, as well as the length of the target DNA. In general, it is supposed that a single polymerase enzyme can bond about a thousand bases every minute, and under the perfect conditions at each elongation step the total nos. of template DNA strands is doubled. Therefore, after the completion of each cycle, the starting amount of DNA is to be doubled exponentially.
Final elongation: After completion of the required thermal cycles, at this penultimate step, the temperature is kept at 70–74° C for 5 to 15 mins. This step is conducted to make sure any leftover single-stranded DNA can be extended completely.
Final hold: At the final step, the reaction centre is finally cooled to 4–15° C and can be stored temporarily.
Real-Time Rt-PCR
The Covid-19 Rt-PCR test has a real-time variation. Real-time Rt-PCR is a modified version for quantifying the amount of DNA amplified after each cycle of PCR using spectrofluorometry. In the reaction mixture, a site-specific probe is added; the most commonly used is the TaqMan probe. It has a fluorescent molecule and a quencher molecule added at two ends. The quencher is a molecule that absorbs any fluorescence from the fluorophore and hence the probe is undetected at the primary stage.
During subsequent steps, the probe attaches itself to the target DNA, but during the elongation step, the probe is denatured by the DNA polymerase, freeing the fluorophore from the quencher. Hence, we can see that as the cycles of PCR progress, more DNA is amplified and more fluorophore is accumulated. This fluorescence is detected and quantified using a spectrofluorometer and thus helps in quantitative analysis.
Time duration for Rt-PCR test result
Typically a Covid-19 test result is available within 24 hours of sampling, but the duration varies depending upon the sample load, the time taken by the sample to reach the testing site, and indication of false test results.
Interpretation of Covid-19 Rt-PCR test results
Studies show the Rt-PCR test gives the most accurate results when tested within 3 days after infection as the viral load slowly decreases after a week of the infection.
A positive test should result in the immediate isolation of the infected person and the administering of proper medication, as advised by a doctor. Most people, like those with asymptomatic infections or those with moderate symptoms, can heal and recover at home without medical intervention.
But one must seek immediate medical care in case of the following symptoms:
- Breathing difficulty
- Confusion
- Chest pain
- Blue coloration of lips or face
- Heavy chest pressure
- Feeling sleepy and drowsy
A negative test result indicates that the person wasn’t infected before the sample collection, but it in no way confirms subsequent infection and hence one should follow strict protocols like social distancing and wearing masks all the time.
What is meant by Ct values for RT-PCR test results?
The Ct-value in an Rt-PCR test result stands for ‘cycle threshold’ of the coronavirus and is an indication of the viral load within the patient. With the emergence of various mutated variants of the SARS-CoV 2 virus and its proximity to human coronavirus, Ct-value is crucial for disease diagnosis.
A Ct-value less than 35 is considered to be a positive result whereas those higher than 35 are negative. Ct-value indicates the numbers of cycles of RT-PCR needed to be run to detect a positive coronavirus. Hence, a cut-off value of 35 indicates a total of 35 cycles of RT-PCR is run before any detectable amount of viral genetic material is found.
A lesser value indicates a higher concentration of viral genes present within the sample and hence deems the person as highly contagious.
Importance of Ct-value
The Ct-value can be indicative of the transmission potential of the person tested. In simple words, a higher concentration of viral materials in one’s throat and nasal cavity means he will more easily spread the virus than those with a lesser value. Hence, it is important in assessing the prevalence of infection in a particular region.
Also, studies indicate that there is no direct link between a lower Ct value with the mortality rate or the severity of the coronavirus infection. It is linked only with the time of infection and onset of the symptoms and infectivity, so there is no need to panic when one gets a lower Ct-value in a Covid-19 test result.
Can the Covid-19 Rt-PCR test differentiate between different mutated variants of SARS-CoV2?
The SARS-CoV2 is a highly mutable strain of the virus and has resulted in various genetic mutated strains, like the Omicron and delta variants.
Presently, the RT-PCR for Covid-19 can only identify the SARS-CoV2 virus broadly and no authorised tests kits to identify mutated strains are available yet.
The mutated species show different serological, antigenic, and genetic properties and can impact the test results. So, it is advised to consider the patient’s history, clinical symptoms, and epidemiological impact even if the test results are negative.
Repeated testing with alternative genetic targets of Covid-19 as authorised by the FDA, is to be done as different variants may contain different genetic markers and can remain undetected.
Conclusion
Rapid and accurate identification of Covid-19 is the primary tool for decreasing the coronavirus pandemic.
One should always be alert by avoiding crowded gatherings and using face masks and monitoring possible symptoms for the safety of oneself as well as the community.
It is very easy to check your RT-PCR test results online, and you get them instantly. In this article, we will learn about how to check RT-PCR reports online, how the RT-PCR test is conducted, what exactly is tested, and how the results are calculated, interpreted, and analysed.
Downloading the RT-PCR app, developed by the National Informatics Centre for ICMR, makes it possible for sampling centres to obtain information regarding the pattern being gathered for Covid. The vaccination certificate download is typically recommended due to the possibility of getting infected even after vaccination and assisting the officers in obtaining the vaccine records.
This application displays positional information from the location where the samples were taken, such as latitude and longitude. With the app being essential to downloading the coronavirus test report, many wonder, “How do I get the RT-PCR report?” Well, if you have been wondering too, here’s what you should know.
What is RT-PCR?
This test helps detect infectious diseases and specific genetic changes quickly and accurately. DNA or RNA is detected in samples to detect the Covid virus.
The only thing capable of reproducing is DNA, which contains instructions and information.
There is also RNA, which is a type of genetic material. A DNA copy, which is involved in the production of proteins, contains information copied from DNA.
DNA and RNA are commonly found in viruses and other pathogens.
PCR tests can detect infection in its earliest stages, unlike many other tests, which may miss early signs of disease because either the virus, bacteria, or other pathogen is not present in the sample in sufficient amounts or your immune system has not developed antibodies yet. You produce antibodies to fight viruses and bacteria through your immune system. You can use PCR tests to detect disease when only very small amounts of pathogens are in your system. Using the Android app, you can quickly find the RT-PCR report online.
The PCR process involves multiple replications of a small amount of genetic material in a sample. During the amplification process, replicated fragments form more copies. Amplification will make pathogens much easier to detect if there are any in the sample.
The RT-PCR app: how to check your RT-PCR report online
- Install the RT-PCR app from the iOS App Store or Google Play Store to view the RT-PCR test report.
- Afterwards, you must provide your mobile number.
- Your phone number has been verified, and the rules and conditions have been agreed to.
- A subsequent OTP will be sent to your provided mobile number.
- Enter the One Time Password (OTP) to begin using the application.
- You will get a list of options, and you need to select “Add a New Patient” from the list.
- To proceed, you will have to fill out the form that asks for your data, including the number from your ID card.
- There are even questions about fitness that you can answer.
- After you have completed the form, click the “Submit” button on the bottom left-hand corner.
How to find an RT-PCR report through the app
- To begin, launch the RT-PCR app on your iOS or Android device.
- You will then be able to see the forms when you select the option.
- To select the date you submitted the form, choose the submission date.
- In that window, you can view the SRF forms, and from there you can select the one you would like to view in PDF format.
- After you click this, you can download the form to the device.
With the help of authorised collection centres throughout India, the Indian government collects information about Covid RT-PCR, rapid antibody tests, and rapid antibody tests,
The website covid19cc.nic.in mainly serves as a portal for authorised persons to enter their credentials to utilise the mobile app to enter RT-PCR, Rapid Antibody, and Rapid Antigen test results via their mobile devices directly into the ICMR portal for samples that are likely positive (+) or negative (-). This portal will only be accessible to government officials. I hope you are clear on how to find the RT-PCR report online. Make use of resources like MyGate to learn more about the RT-PCR report.
How to find the RT-PCR report online?
The websites covid19cc.nic.in and report.icmr.org.in allow you to download RT-PCR reports in PDF format. You have the option to download multiple forms of reports through providing your SRF ID or Mobile Number on this website, and you can get a printed copy of the RT-PCR report online utilising the PDF format. Please find extensive information below about the RT-PCR report download online 2022 process on report.icmr.org.in and details regarding Covid test report download. I hope you are clear on how to find your RT-PCR report online.
RT-PCR report download 2022 PDF
Individuals can download their PCR test report on covid19cc.nic.in. It is a web-based self-service portal for hospitals in India launched by the Ministry of Health to make all test results available across India. Downloading the Covid report can be done by simply entering the user’s SRF ID or Mobile number. Please refer to the steps below for more details on how to complete the RT-PCR report download 2022. This post will briefly discuss the various methods for downloading the Covid rest report 2022. You can now immediately download your report online with a few keystrokes. As we all know, it is sometimes challenging to collect covid test reports.
How to download the RT-PCR Covid test report online 2022 using your mobile number:
- You can access report.icmr.org.in on your mobile device.
- On covid19cc.nic.in., click on the Download RT-PCR SRF pdf format option.
- Finally, enter the OTP you received along with your mobile number.
- The Covid test report can now be viewed online.
- It includes everything you need to know about downloading an RT-PCR report online.
Ways to do the Covid test at home
- RT-PCR tests can be done at home by contacting your local laboratory.
- You can get a spontaneous Covid test report by using an antigen test kit at home as a second possibility.
- An alternative is to purchase a test kit for Instant Results and check your sample.
How to save RT-PCR test reports on your device?
RT-PCR test results can be checked online using the steps above, after which you should click on the Download button under the Action column to view your report. After saving it on your laptop or smartphone, you can view it.
Note:
Compared with the PCR test, the antigen test is usually faster but less sensitive. In some cases, if the antigen test is negative for Covid, your healthcare provider may suggest a PCR test to confirm the result. The antigen test is not as accurate as the PCR test. If you need more information about your RT-PCR report, go to sites like mygate.com.
Slowing the spread of Covid requires accurate and rapid testing. If you experience symptoms, you should contact your healthcare provider or the public health department in your area for suggested testing. Your healthcare provider will determine which test will give you best results in the shortest time span. For the safety of those around you, you should wear a face mask that fits snugly over your nose, mouth, and chin. Additionally, it would be best if you avoided close contact with anyone until the results of your COVID test are available.
Conclusion
You might be infected with SARS-CoV-2 if you have received a positive test result. Infections that cause no symptoms are called asymptomatic infections. Infections that cause symptoms are called symptomatic infections. Most people recover safely at home without medical treatment when they have a mild form of Covid. Your healthcare professional should be contacted if your symptoms worsen or you have questions.
Negative test results indicate that you have probably not been infected with SARS-CoV-2 when the specimen was collected. Covid can, however, be present without being detected by the test. If you’ve had Covid for more than a week before being tested, for example, this could happen if you recently became infected but haven’t exhibited any symptoms yet. Negative tests do not guarantee that you won’t be exposed to Covid afterwards, get infected, and spread the SARS-CoV-22 virus to others.
FAQs
In what way does the Covid testing site collect demographic information about patients?
The CARES Act requires all testing sites to report test results, both positive and negative, for each test they perform to diagnose or detect Covid. The HHS developed this guidance in response to the CARES Act. Covid testing results have been required to be reported by state and local public health departments since the beginning of the Covid public health emergency; however, the requirements for patient information and other data elements vary by state. According to the new HHS guidance, essential data elements, including patient age and zip code, will be reported more frequently in contact tracing, control, and mitigation efforts.
Is the Covid test available anywhere?
There are currently 57 government laboratories that perform the primary test, 51 of them under the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). A complete list of all these laboratories can be viewed here. You can call the state government helplines or the central helplines released by the health ministry, and the staff will direct you to the nearest facility to have your blood drawn.
How does Covid testing work in India?
In India, symptomatic people who have travelled abroad recently are only tested based on a limited and specific protocol.
Since the virus has not been detected in communities, the ICMR notes that the prominent people being monitored are those who have travelled abroad to high-risk countries in the last 14 days and those who have had contact with people in these countries.
The next three weeks are going to be difficult times for all of us. While the government has made clear that we may move out to purchase essentials, it is important that we spend nearly all of our time at home.
This is easier said than done, and self care is crucial to getting through this period. Through discussions with experts and research, we have put together a list of best practices to follow to ensure we take care of ourselves, our families and any others who may be in need of help during the lockdown period.
Stay healthy, stay safe.
DOWNLOAD THE HOME LOCKDOWN GUIDEAbout MyGate
MyGate is India’s largest gated community management app, benefiting thousands of housing societies, developers, society facility managers, and millions of homeowners in every Indian city.
The government has requested that we stay home for the good of society – however, there are times when resident movement is unavoidable for purchase of essentials and medical emergencies. In these times, it is important for the society to be aware of such movements, hence we are highlighting our Resident Entry/Exit Log feature during the coronavirus lockdown.
What is Resident Entry/Exit Log?
Resident Entry/Exit Log is a feature on the guard app that is helping both the committee members and the residents in the following ways:
Committee members:
– Record or restrict the entry of non-residents within the community
– Record logs and trace back, if and when required
Residents:
– Ensure safety of individuals and their families
– Stay aware if a suspect case is identified within the community
How important is this feature for my society?
The feature was built to help the societies monitor any movement in and out of the community during wee hours and only allow residents using their designated MyGate code.
However, with the increasing practice of social distancing amidst Coronavirus, it is observed that many societies are now using it to identify non-residents and ensure safety of those residing within the community.
As per the instructions issued by the Government Authorities, the societies are required to monitor the residents moving in and out of the communities. Many societies in Pune have already implemented the feature. As the government authorities continue to issue the same orders across other states and cities, the feature will become fundamental in helping the communities stay informed and be proactive in curbing the spread.
Keeping in view the current lockdown, we highly recommend this feature to minimise risk and stay alert, while practicing social distancing.
How does it work?
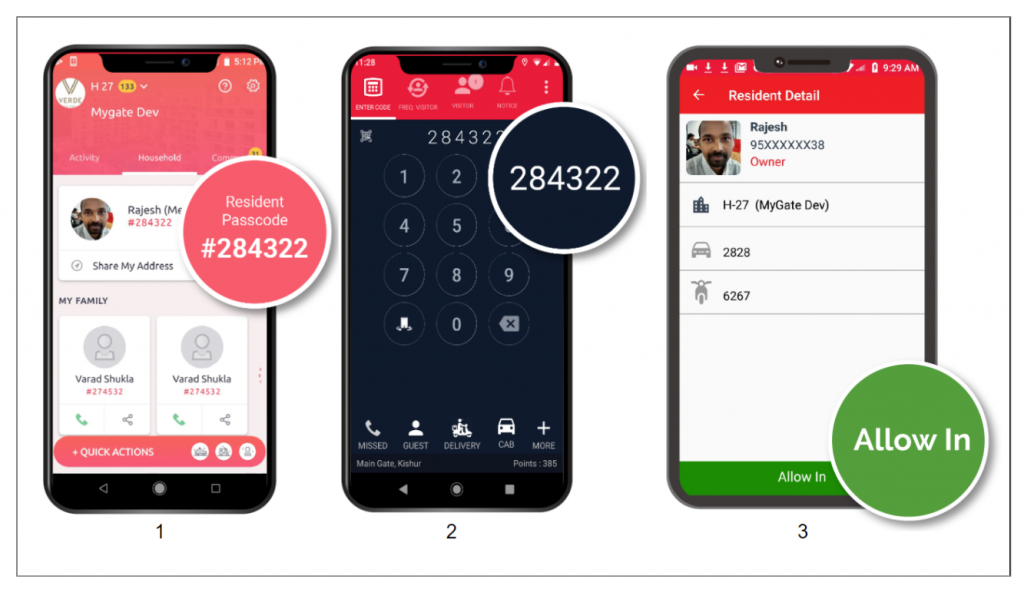
Step 1: The resident needs to share their designated passcode with the guard at the time of the entry
Step 2: The guard will then enter the passcode in the guard app
Step 3: This will reflect the resident details, such as name, flat and vehicle number, on the guard app screen. The guard will then click on the ‘Allow In’ button to approve and record entry.
How can I enable ‘Resident Entry/Exit Log’ for my society?
Please get in touch with your MyGate representative. They will assist you with updating the settings on the MyGate dashboard. In case of any concerns, please write to us at [email protected].
India is at the top of many notorious lists globally. It ranks 13th globally for overall Water Stress Index (denoting high level of baseline water stress). A more alarming fact than this statistic is that India’s population is thrice more than the other countries listed on the chart. So the efforts to combat the water deficit would require thrice the boost from the government as well as the citizens.
The Water Project data states that children in 100 million homes in the country lack water. Water In Crisis – Spotlight India
In urban areas, citizens suffer water scarcity throughout the year, especially in summer, due to lack of proper distribution and freshwater deficit.
The government’s Jal Shakti initiative aims to provide piped water to all households by 2024, while Urban Local Bodies struggle to reform their current water governance.
In the meantime, the only way to tackle this water crisis is to be careful with its usage and conservation.
In 2019, a housing society in Bangalore reduced their Rs 16 lakh water bill by 52%, while a housing complex in Chennai recycled 45,000 litres of sewage for gardening and cleaning.
Eco-conscious citizens across India have taken upon themselves the responsibility of water conservation while showing others how to save water in the most effective way.
Find out below some of their go-to water conservation methods
1. Water Efficient Plumbing Fixtures
A surefire way to make sure you save water during daily chores are water-saving fixtures that can be retrofitted in your current bathrooms and kitchen. For instance, low-flow faucets can be installed with aerators or flow restrictors that can cut down water usage from 2.5 gpm (gallons per minute) to 1.5 gpm. Low flow showerheads should not allow more than 2.5 gpm water flow. Toilets make up 30% of total water usage in a household. Low flush toilets (or high efficiency toilets) use gravity or pressure based systems in order to use as low as 1 gpf (gallons per flush) as opposed to standard 1.6 gpf. Some people also install water saving toilet kits in their existing toilets.
2. Insulated piping
Residents waste water when waiting for hot water through the taps. Insulating pipes and water tanks is part of the government’s Energy Conservation Building Code that was launched in 2007. It saves water while also saving electricity.
3. Smart cleaning equipment
Get rid of the old school mop and bucket and invest in water saving floor cleaning machines, if not for individual homes, at least for cleaning and maintaining common areas like lobbies, reception, staircases. Commercial floor scrubbers with water saving technology can save 50% of water needed to clean large common areas of residential buildings. Alternately, modify existing cleaning equipment with aerated spray nozzles, timer operated shut off valves, flow restrictors in water lines.
4. Dual piping system
With this water conservation method, two independent piping lines are installed, one that supplies potable water and the other that supplies reclaimed water (seawater/greywater) which cannot be consumed but can be used for toilet flushing, car wash, etc. Reclaimed water is treated before it is supplied.
5. High efficiency (HE) appliances
Low water washing machines claim to cut down your annual laundry water usage by 30 to 40%, using only 18-25 gallons per load as opposed to regular ones that use about 50 gallons. Also always use HE laundry detergents in HE machines. Unbeknownst to many people, doing dishes by hand uses more water (approximately 3.5 times more) than a dishwasher; even better if you use an energy star dishwasher with air dry option and a soil sensor.
6. Smart water meter
Install smart water meters for your building in order to track water consumption patterns of each home. Compare water usage of multiple inlets in real time and build a healthy competitive spirit among residents, encouraging and applauding those with lowest consumption. It has been estimated that societies can save up to 35% with water meters.
7. Rainwater harvesting
It’s no secret that groundwater in cities is depleting due to concrete sprawl and it doesn’t make practical sense to pay huge amounts of money for water tankers every month when rainwater harvesting can be done on rooftops. Water from rooftop catchment is then directed through pipes to be filtered and then stored in basement storage tanks. Depending on the size, installation can cost anywhere between Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh.
8. Sewage treatment
Many residential buildings in India already have their own sewage treatment plant (STP). If your society gets together and invests in one, it would mean recycled water 365 days a year and zero water scarcity. You’d have to get a consent for operation from your municipal corporation, employ qualified staff for standard operating protocol so that the STP can operate efficiently. However, invest in an eco-friendly STP that doesn’t require diesel to operate and functions on anaerobic method, requiring low energy and mimicking natural processes. One-time investment in an STP can cost up to Rs 14 lakh but since it’s self sustaining, the ROI is excellent. Another option is to invest in an Omni Processor that is already made on self sustainable principles and produces electricity as well as potable water. This investment not only solves the water/electricity crisis, but also reduces the amount of raw sewage being dumped into rivers and lakes, which helps in preventing diseases and protects the environment.
9. Greywater recycling
Reuse at least 50% of daily water with this conservation technique. Attach a diverter pipe with a valve to your existing piping of kitchen/ bathroom sinks, laundry and shower. All greywater runs into a tank with a submersible pump that runs the water into a tank to be reused for toilet flushing after being cleaned with cleaning agents. Alternately, connect pipes to greywater drains and let them flow into flower beds and gardens which also help groundwater recharging. You can store all your greywater in a large tank and install a purifier to repurpose all the water for various cleaning applications as well.
10. Green landscaping
Your society’s garden does not require fresh water throughout the summer if you combine a number of water conservation techniques diligently. To begin with, try Xeriscaping your garden which involves growing low water consuming shrubs and plants which can be an alternative to high maintenance lawns that consume too much water. You can reuse greywater to water plants manually even if drain pipes from homes don’t run straight to the garden. Instead of ornamental, exotic, high value plants and flowers, grow native plants and local wildflowers that adapt to the regional climate in every season and consume less water. Remove the underground sprinkler system and try a drip irrigation system along the garden border to slowly feed the plants with required water. Create a rock garden instead of maintaining a traditional lawn turf. Do away with garden hoses and switch to manual watering. Place mulch around your plants to stop water evaporation by 50%.
Pro tips to save water this summer (and throughout the year)
- Shorten your showers at least by 5 minutes.
- Alternately, prefill one or two buckets and use only that amount to take a shower.
- Use your dishwasher and washing machines for full loads only.
- Don’t let the water run through the tap while brushing your teeth, washing hands and face.
- Opt for eco car wash (waterless car wash or high pressure steam cleaning) instead of using pipes in the parking lot.
- Regularly check taps, showers, water fixtures for leakages.
- Educate the help, service, and maintenance staff in your home as well as the building to be vigilant while using water for cleaning purposes.
- Instruct children to not waste water when in the toilet or while taking showers.
- If you have plants on your balcony, water them during the morning or evening for increased water retention.
- Build temporary soil mounds and slopes with native plants in your garden to retain water.
- Use micro-sprinklers for your lawn (if you choose to keep the lawn).

